Table of Contents
What are the Adopter Categories?
Adopter categories divide consumers into sections based on their willingness to try out an innovation or product.
Adopter categories can be defined as in-between product adopters based on time and level of willingness with which they tried or will try the product/service. And also, it breaks the customer adoption journey over a while. Adopters are customers who have ongoing using or exploring product offerings.
Market researchers have secret consumers into five categories based on their product adoption during different stages of that product’s life cycle.
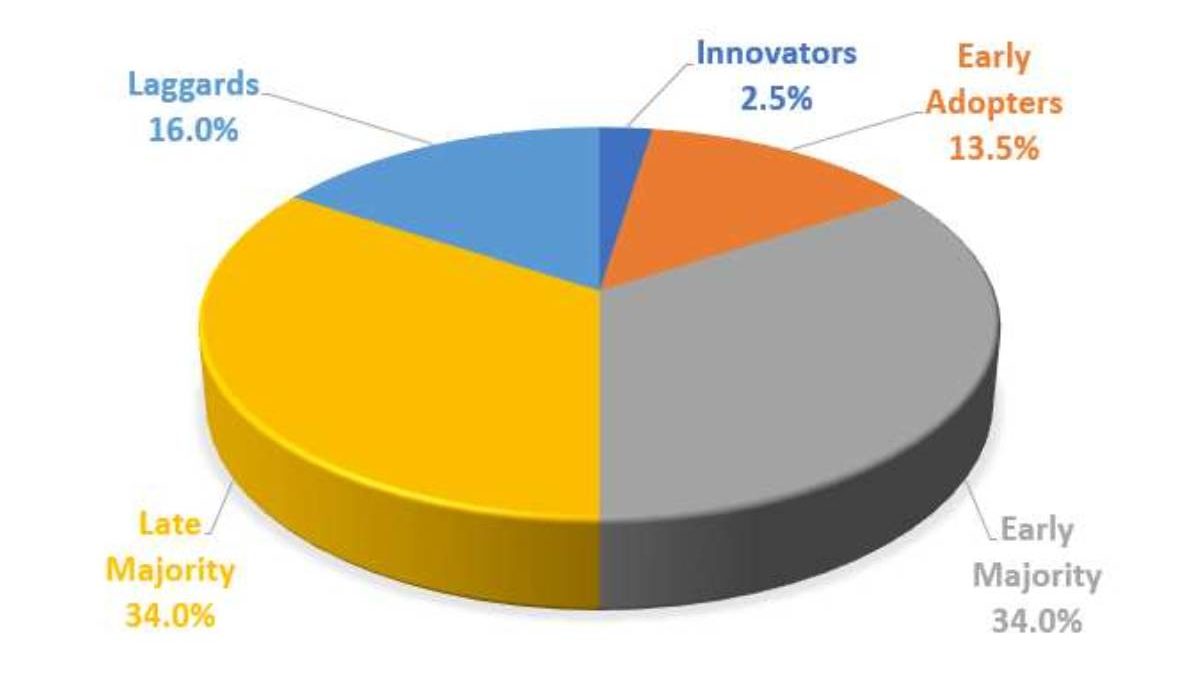
And also, the five adopter categories are Innovators, Early adopters, Early majority, Late majority and Laggards. Adopter categories define as a part of the Diffusion of Innovation Theory.
Understanding Adopter Categories
- As a term, Adopter categories are part of the diffusion of innovations theory. They have been applied to several studies, including marketing, organizational studies, knowledge management, communications, and complexity studies.
- The adopter categories were first named and labelled in the landmark book Diffusion of Innovations by sociologist Everett Rogers in 1962.
- A rendering to his research shows five adoptive parent categories—innovators, early adopters, early majority, late majority, and laggards.
- Rogers identified each adopter category’s critical characteristics, such as the fact that early adopters have the highest degree of view leadership among the adopter categories.
- At the same time, the laggards are likely to be older, conservative, and more price-conscious.
- And also, the concept of adopter categories widely uses in present-day marketing, especially for revolutionary new products or facilities.
- For example, adopter categories are particularly relevant to social network analysis.
Types of Adopter Categories
The five types of adopters comprise:
-
- Innovators
- Early Adopters
- Early Majority
- Late Majority
- And also, Laggards
1. Innovators
- Of the five adopter categories, individuals in the Innovators category represent only about 2.5% of operators.
- Innovators are technology fans that are willing to take risks on a new offering. Usually, they have a high social status and often consider mavens in their space or industry.
- Of the five adopter categories, Innovators have a high degree of financial liquidity to engross disappointments.
- And a high-risk tolerance that lets them adopt new technologies that may ultimately fail.
- They connect socially to engineers and technicians, and they often interact with other innovators.
2. Early Adopters
- Of the five adopter groups, individuals in the Early Adopters group signify about 13.5% of operators.
- They are visionaries and view bests in their space or industry.
- And also, primary Adopters have a high degree of social rank that allows them to influence others based on their opinions.
- They are more likely to feast the word than Innovators with their followers.
- Early Adopters are a bit more discriminating in their adoption choices than Innovators to help them maintain the central communication position they enjoy.
NOTE: Innovators and Early Adopters primarily focus on technology and presentation. A kind of chasm exists between Innovators and Early Adopters, and other adopters since other adopters emphasise solutions and convenience rather than technology and performance.
Companies’ central pivot is necessary to refocus the marketing message to cross from Early Adopters to the Early Majority.
3. Early Majority
- Of the five adopter groups, individuals in the Early Majority category signify about 34% of users.
- The Early Majority adopt an innovation long afterwards, Innovators and Early Adopters.
- And also, the Early Majority focuses on solutions and convenience over technology and performance and, therefore, delay the technology to mature.
- While the Early Majority has above regular social status and contact with Early Adopters, they seldom are opinion leaders.
4. Late Majority
- Of the five adopter categories, persons in the Late Majority signify about 34% of operators. And also, the Late Majority accept an innovation much later in a technologies maturity cycle.
- Late Majority individuals method an innovation with a high degree of scepticism and adopt the design only after most of society has already accepted it.
- And also, the Late Majority often has slight financial liquidity, so their risk tolerance is low, affecting others.
5. Laggards
- Of the five it, persons in the Laggards group represent the final 16% of users.
- Laggards are dead last to accept innovation. Laggards typically have an aversion to change, inclined to focus on “traditions”.
- They are generally only persuaded to embrace technology by close friends and family.
Examples of Adopter Categories
- Innovators: People who are and will be crowding Apple stores for the Apple watch.
- Early adopters: Persons in India who are now exploring e-commerce.
- Early majority: People using cloud facilities.
- Late majority: People who have just ongoing using debit/credit cards.
- And also, Laggards: Those who buy Apple iPhone 4(concerning iPhone, these people are laggards).
Conclusion
It divides consumers into parts based on their willingness to try out an innovation or product.
As a term, Adopter categories are part of the Diffusion of Innovations Theory. They have been applied to several studies, including marketing, organizational studies, knowledge management, communications, and complexity studies.
And also, the adopter categories were first called and described in the landmark book Diffusion of Innovations by sociologist Everett Rogers in 1962.