Table of Contents
Storage Area Network Definition
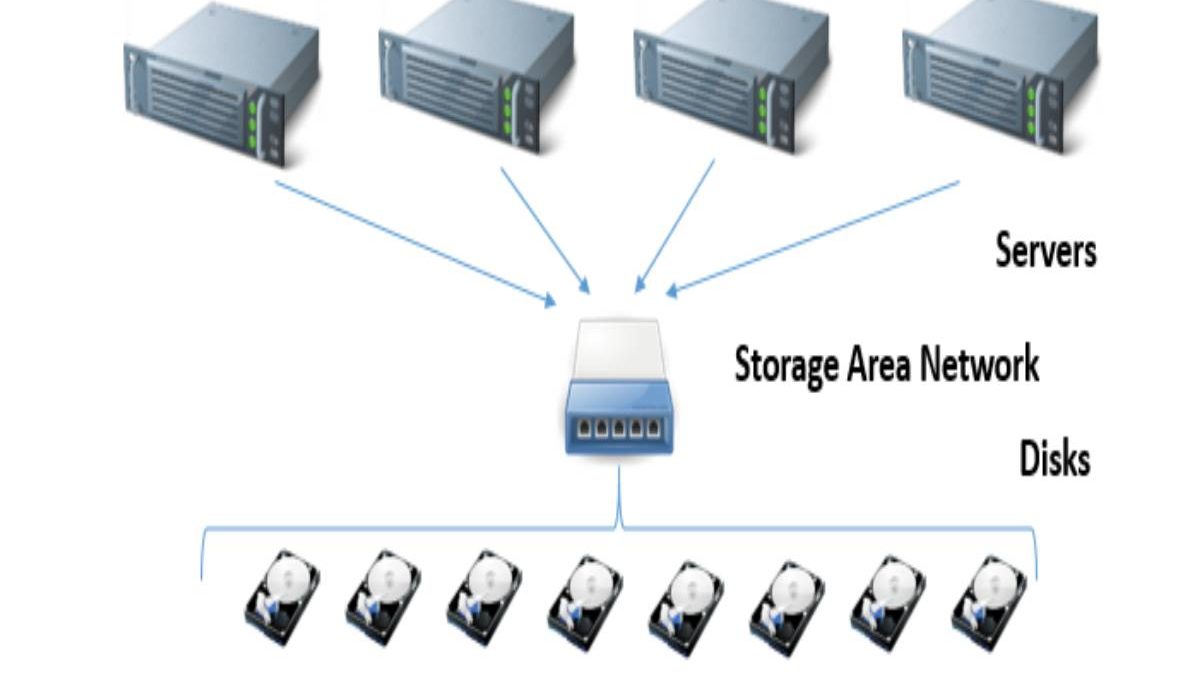
A storage area network (SAN) a dedicate high-speed network (or subnet) that interconnects and presents shared pools of storage devices to multiple servers.
A SAN displaces storage resources from the standard user network and reorganizes them into a separate, high-performance network.
It allows each waiter to access shared storage as if it were a drive directly attached to the server. When a host wants to admission a storage device on the SAN, it sends a block-based access request for the storage device.
A storage area network is typically assembled using three main components: cabling, host bus adapters (HBAs), switches, or switches. Every switch and storage system in the SAN must interconnect, and the physical interconnects must support bandwidth levels that can adequately handle peak data activities.
Concept of Storage Area Network
- Storage area networks centrally manage, and Fiber Channel (FC) SANs can be expensive, complicated, and challenging to manage.
- The advent of iSCSI reduce these challenges by encapsulating SCSI commands in IP packets for broadcast over an Ethernet connection rather than an FC connection.
- In its place of learning, building and managing two networks – an Ethernet local area network (LAN) for user communication and an FC SAN for storage.
- An organization can now use its existing information and infrastructure for both LANs and SANs.
What are the Types of Storage Area Network?
Virtual Storage Area Network
- A virtual storage area network a software-defined storage offering deploy on top of a hypervisor such as VMware ESXi or Microsoft Hyper-V. Virtual SANs provide some benefits, such as ease of management and scalability. For the most part, VSANs are hardware agnostic.
- As long as the hypervisor’s storage hardware recognises and supports the hardware, VSAN (although each vendor has its requirements).
Unified Storage Area Network
- A unified SAN is based on the concept of unified storage, which exposes file and blocks storage through a single device (typically a modified NAS device).
- A unified SAN takes this concept one step further by exposing the numbers of dedicated logical units (LUNs), like any other SAN and the NAS-based file system.
Converged Storage Area Network
- Storage area networks typically keep separate from Ethernet networks. A converged SAN uses a shared network infrastructure for SAN and network traffic to eliminate redundant infrastructure and reduce cost and complexity.
- SAN networks often use FC, while data networks often Ethernet-base. The converged networks adopt Fiber Channel over Ethernet (FCoE), which encapsulates Ethernet frames loads FC.
- Converged SAN networks almost always based on 10 Gigabit Ethernet, and multiple network ports sometimes link to increasing performance.
The Pros and Cons of Storage Area Network
- The main benefit of using a SAN is that raw storage is treated as a set of resources centrally managed and allocated. SANs are also highly scalable because extra capacity can add as required.
- The main disadvantages of SANs are cost and complexity. SAN hardware tends to be expensive, and structure and managing a SAN needs a specialized skill set.
Storage Area Network (SAN) vs Network Attached Storage(NAS)
- The terms SAN and NAS occasionally confuse each other because the acronyms are so similar. NAS consists of a storage device that connects directly to a network switch. Although there are exceptions, NAS devices often use as file servers.
- A SAN is much more complex and expensive than NAS. A SAN consists of dedicated cabling (typically FC, but Ethernet can use in iSCSI or FCoE SANs), dedicated switches or switches, and storage hardware.
- SANs are highly scalable and let storage to expose as a LUN. In contrast, NAS storage typically exposes the repository as a file system, although some NAS devices support block storage.
The traffic of Storage Area Network
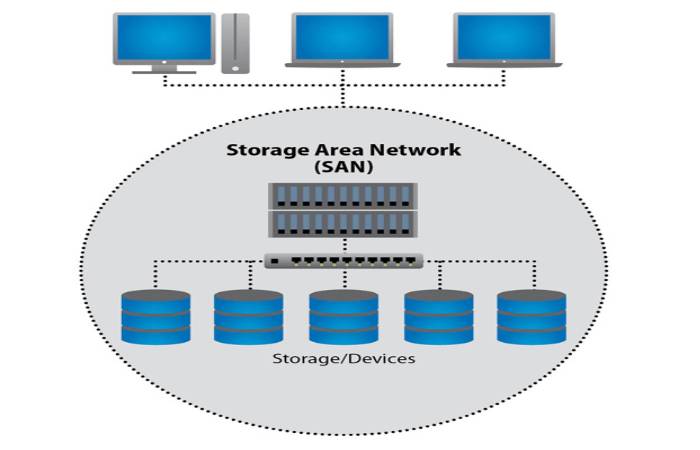
The type of traffic in a SAN is very similar to hard drives such as ATA, SATA and SCSI. Most of today’s SANs use the SCSI protocol to access data from the SAN, even though they do not use physical SCSI interfaces.
Latency
- One of the main differences and characteristics of SANs is that they build to minimize the transmission medium’s response time.
Connectivity
- Allows multiple servers to connect to the same disk group or tape libraries, enabling optimal utilization of storage systems and backups.
Distance
- SANs being built with fibre optics inherit the benefits of this. For example, SANs can have devices with a separation of up to 10 km without routers.
Speed
- Any computer system’s performance will depend on its subsystems’ speed, which is why SANs have increased their information transfer speed, from 1 Gigabit to currently 2 and 4 Gigabits per second.
Availability
- One of the advantages of SANs is that by having more excellent connectivity. They allow servers and storage devices to connect more than once to the SAN. In this way, you can have redundant routes that, in turn, increase tolerance to failures.
Components
- The primary components of a SAN are switches, directors, HBAs, servers, routers, gateways, disk arrays, and tape libraries.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Storage Area Network
- The performance of the SAN directly relates to the type of network that it uses. For a Fiber Channel network. The bandwidth is approximately 100 megabytes/second (1,000 megabits/second) and can extend by increasing the number of access connections.
- A SAN’s capacity can extend almost unlimitedly and can reach hundreds and even thousands of terabytes.
- A SAN allows data to share among multiple computers on the network without affecting performance. Because SAN traffic wholly separate from user traffic.
- They are the application servers that function as an interface between the data network (usually a fibre channel). And the user network (usually Ethernet).
- On the other hand, a SAN is much more expensive than a NAS since the former is a complete architecture that uses technology that is still very expensive.
- Typically, when a company estimates TCO (Total Cost of Ownership) against cost per byte, the cost can be more easily justified.
Conclusion
The storage area network design to connect servers, disk arrays, and support libraries. It is primarily based on fibre channel technology and, more recently, on iSCSI.
Its function is to quickly, safely and reliably connect the different elements that make it up. And it distinguishes it from other network storage modes by the low-level access mode.
Also Read: How to Stream Live on YouTube with Open Broadcast Software(OBS)